
Final Project: Enterprise Data Architecture & Operations for DigiHealth
Estimated time: 1.5 hours
Introduction
DigiHealth is a sophisticated Health Management System (HMS) that automates hospital operations, improves patient record management, and offers robust analytics.
The system effectively manages real-time transactions, such as patient registration, billing, doctor appointments, and medical history, to facilitate smooth operations in healthcare institutions.
As it grows, DigiHealth is increasingly confronted with data scalability, security, and sophisticated analytics challenges.
To meet these complexities, DigiHealth needs a robust Enterprise Data Architecture and a clearly defined Operational Strategy.
The enterprise data architect role will be instrumental in streamlining system performance, maintaining data integrity, and facilitating the platform's sustained growth.
Primary responsibilities of an Enterprise Data Architect
1. Design and implementation of scalable data models
Develop and maintain OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) systems for real-time data handling.
Design OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) systems to support business intelligence and analytics.
2. Data governance and security
Establish and enforce data security protocols, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Define policies for data integrity, access control, and compliance with industry regulations.
3. Development of ETL pipeline
- Design and implement Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes to facilitate efficient data integration and movement across systems.
4. Query performance optimization
- Fine-tune SQL queries and database performance to enhance the efficiency of both real-time and analytical workloads.
5. Implementation of data warehouses and data lakes
- Architect and manage data warehouses and lakes to enable scalable, data-driven decision-making.
Learning objectives
Design a scalable Enterprise Data Architecture by creating ER diagrams, identifying entities, and implementing normalization techniques.
Develop OLTP and OLAP schemas by implementing MySQL-based transactional databases and Postgres-based OLAP schema.
The project is divided into two parts, which are to be submitted sequentially:
Part 1: Implementing Enterprise Data Architecture for data scalability, governance, and optimization.
Part 2: Applying OLTP to OLAP transformation for healthcare analytics and data-driven decision-making.
Part 1: Implementing Enterprise Data Architecture for data scalability, governance, and optimization.
Objective: Design and develop a structured OLTP database for DigiHealth by creating ER diagrams and identifying key entities and relationships. The learners will apply normalization techniques to optimize data integrity and eliminate redundancy.
Tasks
Perform the following tasks:
Task 1: Design an Entity-Relationship (ER) Diagram for DigiHealth's OLTP system.
Determine the core entities in the healthcare system: Patients, Doctors, Appointments, Medical records, and Billing.
Establish the relationships between these entities, including one-to-many (e.g., one doctor handles multiple patients), many-to-many (e.g., various doctors consulting a patient), and one-to-one (e.g., a single medical record per patient).
Define attributes for each entity, ensuring they include relevant data fields (e.g., Patient Name, Date of Birth, Appointment Date, Treatment Cost).
Apply normalization techniques:
First Normal Form (1NF): Ensure that all tables contain atomic (indivisible) data values and have a unique identifier (primary key).
Second Normal Form (2NF): Remove partial dependencies by ensuring all non-key attributes entirely depend on the primary key.
Third Normal Form (3NF): Eliminate transitive dependencies to prevent data redundancy and ensure efficient data retrieval.
Develop a visual representation of the database structure by mapping tables, attributes, and relationships.
Ensure the ER diagram accurately reflects how patient records, doctor appointments, billing, and medical history interact within the system.
Use primary keys, foreign keys, and cardinality to define transparent relationships between entities.
Definitions:
Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs): Visual representations of data structure, showing entities, relationships, and attributes in a database.
Entities: Objects or concepts in a database that store data and have unique identifiers.
Relationships: Connections between entities defining how they interact.
Normalization techniques: Rules (1NF, 2NF, 3NF) that reduce redundancy and improve data integrity by organizing database tables efficiently.
Part 2: Applying OLTP to OLAP transformation for healthcare analytics and data-driven decision-making.
Objective: Design and implement a scalable data architecture for DigiHealth by developing a structured OLTP database in MySQL for real-time transactions and transitioning to an OLAP data warehouse in PostgreSQL. Learners will define relational schemas, create Fact and Dimension Tables, and apply data modeling techniques to support advanced healthcare analytics.
Tasks
Perform the following tasks
Task 1: Designing the OLTP Schema (Transactional Database in MySQL)
Develop a structured OLTP database in MySQL (prepare CREATE TABLE statements) to support real-time transactions based on the tables designed in the ERD in Part 1_Task 1.
Define database tables with appropriate relationships, keys, and constraints, ensuring data consistency and integrity.
Also, develop INSERT scripts for the OLTP database.
Task 2: Designing the OLAP Schema & Data Warehouse (Analytical Model in PostgreSQL)
Choose and implement a suitable data warehouse schema, either Star Schema (simpler structure with fewer joins) or Snowflake Schema (more normalized and efficient for complex queries).
Create Fact Tables to store transactional data, of the OLTP database designed in Part 2_Task 1.
Develop Dimension Tables to categorize and describe Fact Tables.
Also develop INSERT scripts for the OLAP database.
Submit a data warehouse implementation report with the following artifacts:
ERD of data warehouse
CREATE & INSERT scripts
Clear documentation of dimensional tables
Any data ingestion/ ETL pipeline diagram from OLTP to OLAP
Below is the reference dimensional model for your OLAP schema.
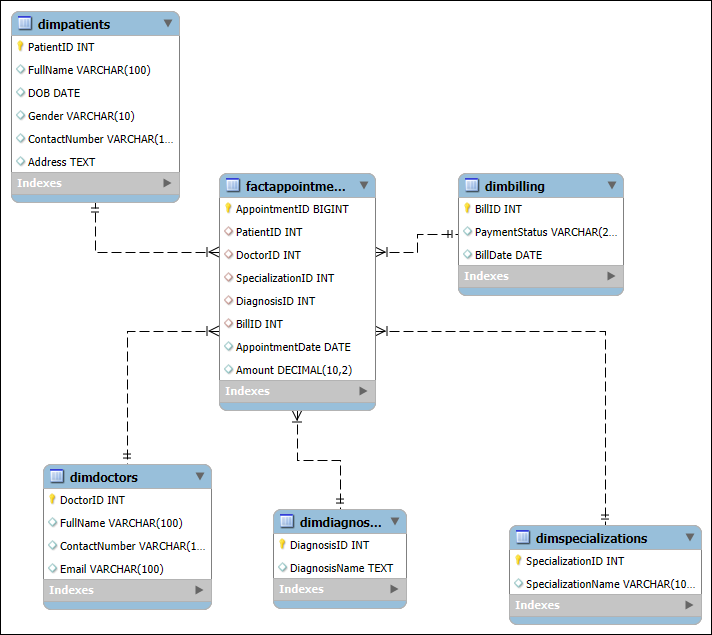
Definitions:
OLTP schema: A database structure optimized for real-time transactions, ensuring fast inserts, updates, and deletes.
OLAP schema: A data model (Star/Snowflake) designed for analytical queries, enabling efficient reporting and decision-making.
Data warehouse: A centralized repository that stores structured data for analysis, supporting business intelligence and reporting.
Final deliverables
You will need to submit the following:
Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) and Normalized OLTP Schema as a visual representation of database design. Upload a screenshot of the diagram named Part 1_Task 1.pdf.
MySQL scripts for implementing the OLTP schema, including CREATE and INSERT scripts. Upload a sql file named Part 2_Task1.sql.
PostgresSQL scripts for implementing the OLAP schema, including CREATE and INSERT scripts. Upload a sql file named Part 2_Task2A.sql.
Data warehouse implementation report detailing schema design, Fact and Dimension Tables, and data transformation processes. Upload a pdf document named Part 2_Task 2B.pdf.
Conclusion:
Congratulations! You have successfully implemented Enterprise Data Architecture for DigiHealth, optimizing scalability, security, and analytics. Your work includes designing a robust ERD for seamless OLTP interactions, applying normalization for data integrity, and developing a MySQL transactional database for real-time operations. You also built a PostgreSQL data warehouse with Star/Snowflake Schema for analytics, ensuring data governance with RBAC and audit trails. This strengthens DigiHealth's ability to manage complex data, enhance performance, and drive data-driven healthcare decisions.